Understanding the IPTV Ecosystem
What is Internet Protocol Television (IPTV)?
Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) is a technology that enables the transmission of television signals through networks based on internet protocol (IP) instead of using traditional methods like satellite, cable, or terrestrial broadcasts. This revolutionary technology converts traditional television signals into digital data packets that are transmitted through IP networks, allowing for a more flexible and personalized viewing experience.
Technical Foundations
IPTV uses the IP protocol to deliver video and audio content as data packets through broadband networks. Unlike traditional television, where all channels are transmitted simultaneously and the viewer simply selects which channel to watch, IPTV transmits only the channel or content specifically requested by the user, thus optimizing bandwidth usage.
IPTV technology supports multiple video formats, from standard definition (SD) to 4K Ultra HD, and can dynamically adapt to network conditions and the capabilities of the user's device to provide the best possible quality.
Key Features of IPTV
- Bidirectional transmission that enables interactivity
- Personalized content distribution based on demand
- Support for multiple devices (Smart TVs, mobiles, tablets)
- Advanced functionalities such as pause, rewind, and recording
- Scalability to add new services and functions
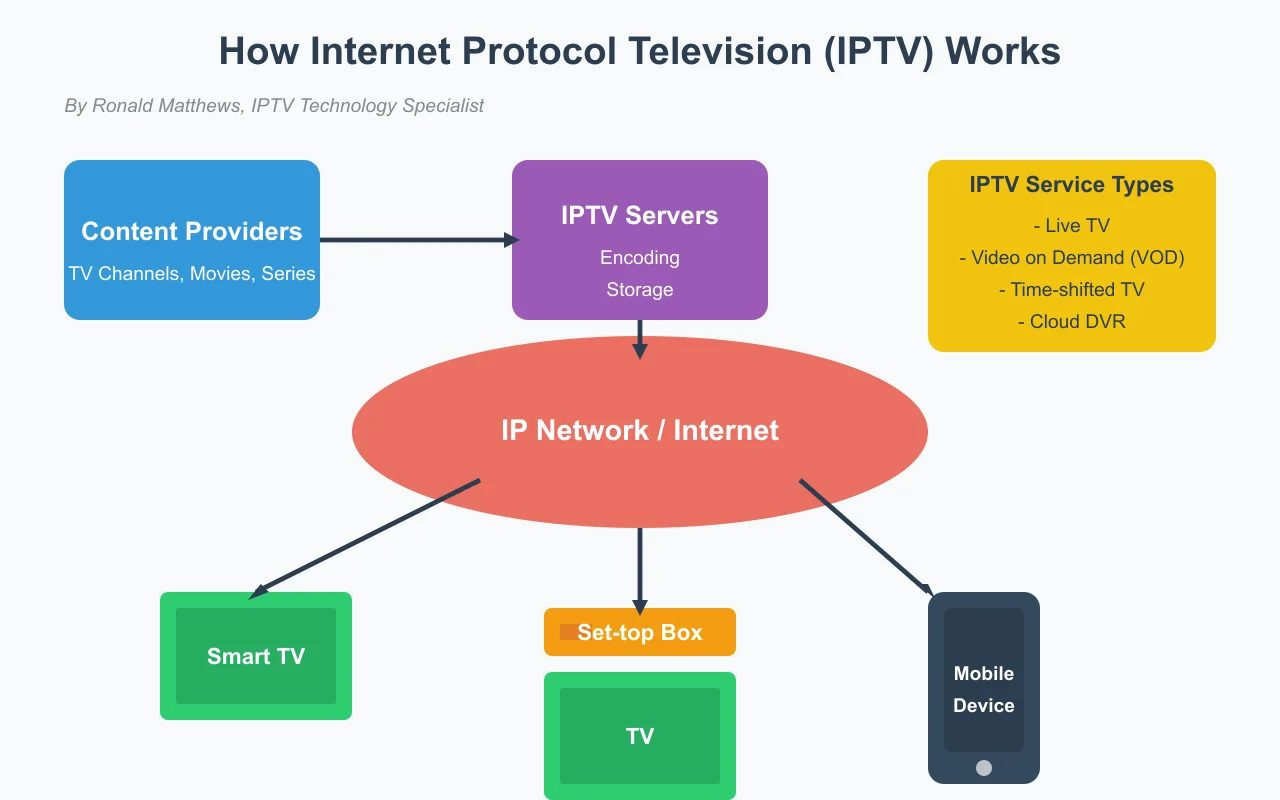
How Does IPTV Work?
-
Content Acquisition
The process begins with acquiring television content from various sources, such as broadcasters, film studios, or content creators. This content can be live (such as sports events or news) or pre-recorded (movies and series). -
Processing and Encoding
The content is processed and encoded into digital formats compatible with IP transmission. This includes video compression using codecs such as H.264 or H.265 to reduce file size without significantly compromising quality. -
Server Storage
The encoded content is stored on specialized servers. Live content is processed in real-time, while on-demand content is indexed and organized in databases for easy retrieval. -
Distribution
When a user requests content, the request is processed through a content delivery network (CDN) that optimizes delivery based on the user's geographic location, network conditions, and other factors. -
Reception and Decoding
The content reaches the user's device (Smart TV, Set-top box, smartphone, etc.) where it is decoded and displayed on the screen. The device requires software capable of interpreting IPTV protocols and decoding the content.
Types of IPTV Services
| Service Type | Description | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Live TV | Real-time transmission of television channels over the internet | Similar to traditional TV but with additional functions such as pause and rewind |
| Video on Demand (VOD) | Content library available to watch whenever the user wishes | Movies, series, documentaries accessible at any time |
| Time-Shifted TV | Allows viewing previously aired programs without having recorded them | Catch-up TV, reruns, content from the last 7-30 days |
| nPVR (Network Personal Video Recorder) | Recording content on remote servers instead of local devices | Cloud recording, unlimited capacity, access from any device |
Technological Advances in IPTV
IPTV technology continues to evolve with developments such as adaptive streaming, which adjusts video quality in real-time according to network conditions, and integration with artificial intelligence systems to offer personalized recommendations and improve the user experience.
IPTV technology forms the foundation upon which IPTV providers build their services, which are then offered to users through different subscription models.
What is an IPTV Provider?
An IPTV provider is a company or organization that offers television services through Internet Protocol (IP). These providers act as intermediaries between content creators and end users, managing the technical infrastructure necessary to transmit television programming, movies, and other audiovisual content over the internet.
Role of IPTV Providers
IPTV providers play a crucial role in the internet television ecosystem. They are responsible for acquiring content rights, maintaining server and network infrastructure, managing customer relationships, and ensuring a smooth user experience. Legitimate providers operate with appropriate licenses to distribute content, complying with copyright and applicable regulations.
Depending on their size and scope, IPTV providers can offer local, national, or international content, and their catalog can range from a few hundred to thousands of channels and on-demand titles.
Key Responsibilities of an IPTV Provider
- Content acquisition and rights negotiation
- Maintenance of technical infrastructure and servers
- Application development for different devices
- Management of customer relationships and technical support
- Ensuring service quality and streaming stability
Types of IPTV Providers
Telecommunications Operators
Established telecommunications companies that have expanded their services to include IPTV, often as part of “triple play” packages (internet, phone, and television). These providers typically operate over managed networks to ensure service quality.
Examples: AT&T TV, Verizon Fios TV, Movistar TV
OTT (Over-The-Top) Services
Providers that offer TV content directly through the public internet, without using managed networks. Although technically different from pure IPTV, these services are commonly grouped under the IPTV category by many consumers.
Examples: Hulu + Live TV, YouTube TV, Sling TV
Specialized IPTV Providers
Companies dedicated exclusively to offering IPTV services, often focused on specific niches such as international content, sports, or particular genres.
Examples: DAZN (sports), fuboTV (sports and entertainment)
Regional Operators
Smaller providers that focus on specific geographic markets, offering content relevant to local audiences along with international channels.
Examples: Local providers operating in specific regions or countries
Technical Infrastructure of an IPTV Provider
IPTV providers maintain complex infrastructures that include:
- Content acquisition systems: To obtain television signals from various sources
- Encoding platforms: To convert content into formats suitable for streaming
- VOD and live streaming servers: For storing and distributing content
- Content delivery networks (CDN): To optimize content delivery
- Subscriber management systems: To manage accounts, billing, and permissions
- IPTV middleware: Software that connects system components and provides the user interface
How to Choose an IPTV Provider
| Criterion | What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Legality | Verify that the provider has appropriate licenses to distribute the offered content |
| Content Selection | Evaluate the quantity and quality of channels and VOD content relevant to your interests |
| Streaming Quality | Check available resolutions (HD, Full HD, 4K) and service stability |
| Compatibility | Ensure it works with your preferred devices (Smart TV, mobile, tablet, etc.) |
| Technical Support | Evaluate the availability and quality of customer service |
| Price | Compare costs with the amount of content and features offered |
Warning About Unauthorized Providers
It's important to distinguish between legitimate IPTV providers and those operating without appropriate licenses. Unauthorized providers may offer suspiciously low prices for a large number of channels, but they present risks such as:
- Inconsistent service quality and frequent interruptions
- Potential legal issues for users
- Absence of adequate customer support
- Security and privacy risks
IPTV providers are the vital link that connects IPTV technology with end users, offering different types of subscriptions according to the needs and preferences of each customer.
What is an IPTV Subscription?
An IPTV subscription is a commercial agreement between a user and an IPTV provider that grants access to television content over the internet for a specified period. These subscriptions define what content will be available to the user, at what quality, on how many simultaneous devices, and what additional functionalities are included in the service.
Components of an IPTV Subscription
IPTV subscriptions vary widely in terms of what they offer, but generally include a defined set of live channels, access to on-demand content, and functionalities such as cloud recording or program restart. Users pay a fee (usually monthly or annually) to maintain their access.
Unlike traditional cable television that often requires long-term contracts, many IPTV subscriptions offer greater flexibility by allowing monthly payments without prolonged commitment, making it easier for users to try different services.
Common Elements in IPTV Subscriptions
- Channel packages (basic, premium, thematic)
- Access to VOD libraries with movies and series
- Advanced features such as pause, rewind, recording
- Limit of simultaneous devices (usually 1-5)
- Duration of service (monthly, quarterly, annual)
- Different quality levels (SD, HD, 4K)
IPTV Subscription Models
Tiered Subscriptions
Many IPTV providers offer different subscription levels, from basic packages to premium options with more channels and features.
- Basic: Essential channels at a reduced price
- Standard: Wider selection of channels and some additional features
- Premium: Wide range of channels, including premium sports and movies, plus all features
Thematic Subscriptions
Specialized packages that focus on specific content categories according to user interests.
- Sports: Focused on sports channels and events
- Entertainment: Series, movies, and variety shows
- Children's: Content suitable for children of different ages
- International: Channels from specific countries or regions
Pay-Per-View (PPV) and TVOD
In addition to regular subscriptions, many IPTV providers offer pay-per-view options for specific premium content.
- Sports events: Boxing matches, important games
- Movie premieres: Films recently out of theaters
- Concerts: Live musical performances
- Special events: Galas, award ceremonies
Free Trials
Many providers offer trial periods so users can evaluate the quality and content of the service before committing to a paid subscription.
- Limited duration: Generally between 24 hours and 7 days
- Full or partial access: Some trials offer all content, others just a sample
- No commitment: Easy cancellation before the trial period ends
Legal Aspects of IPTV Subscriptions
When contracting an IPTV subscription, it's essential to verify the legality of the service. Legitimate subscriptions:
- Operate with appropriate licenses to distribute the offered content
- Have clear and transparent terms and conditions
- Provide an invoice or payment receipt
- Offer customer support and verifiable communication channels
- Maintain privacy policies compliant with applicable legislation
| Subscription Type | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly | Flexibility, low initial commitment, easy cancellation | Higher monthly price, possible activation fees |
| Quarterly | Reduced price compared to monthly, moderate commitment | Less flexibility, larger advance payment |
| Annual | Better price per month, significant long-term savings | High initial commitment, larger upfront investment |
| Multi-user | Allows sharing access with family or friends, divided cost | Higher base price, possible restrictions on simultaneous use |
IPTV subscriptions are constantly evolving, adapting to new technologies and changes in user consumption habits. The current trend points toward increasingly personalized experiences, with advanced recommendation algorithms and enhanced interactivity options.
The television landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years. As a technology enthusiast who's been deeply immersed in the world of digital content delivery for over a decade, I've had a front-row seat to this revolution. Internet Protocol Television, or IPTV as it's commonly known, stands at the forefront of this transformation, fundamentally changing how we consume media content. In this comprehensive guide, I'll share my expertise on what IPTV is, how it works, and why it's becoming the preferred choice for viewers worldwide.
Understanding Internet Protocol Television: The Fundamentals
What is IPTV?
IPTV stands for Internet Protocol Television. At its core, Internet Protocol Television is a system that delivers television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Unlike traditional broadcast, cable, or satellite TV, IPTV uses the internet to stream video content directly to viewers. This technology allows users to stream media content directly to their devices, offering unprecedented flexibility and control over the viewing experience.
As someone who's worked extensively with various IPTV systems, I can tell you that the primary difference between IPTV and conventional television delivery methods lies in how the content reaches your screen. Traditional TV broadcasts content in real-time that you either watch when it's broadcast or record for later. IPTV, on the other hand, stores programming on servers, allowing you to request and watch content whenever and wherever you choose.
The Evolution of IPTV Technology
The journey of IPTV from concept to mainstream technology is fascinating. In the early 1990s, digital TV signals required massive bandwidth, which hindered the development of video-on-demand (VOD) services. However, technological breakthroughs soon changed the landscape.
The term “IPTV” first appeared in 1995 with Precept Software's IP/TV product, which paved the way for audio and video traffic over IP networks. By 1998, U.S. West launched TeleChoice, marking the first U.S. IPTV service. Kingston Interactive Television (KIT) debuted in 1999, influencing UK IPTV regulations.
As internet speeds increased and compression technologies improved, IPTV became more viable. Motion-compensated DCT compression significantly reduced bandwidth needs, shrinking digital TV signals from 200Mbit/s to just 2Mbit/s. ADSL technology improved copper wire bandwidth from 0.1Mbit/s to 2Mbit/s, further enhancing IPTV's feasibility.
By 2005, SureWest Communications was offering the first high-definition IPTV channels in North America, followed by global expansion with services launching in Australia and Sweden. The growth continued, and by 2015, paid IPTV users in Western Europe surpassed pay satellite TV subscribers, cementing IPTV's place in modern entertainment.
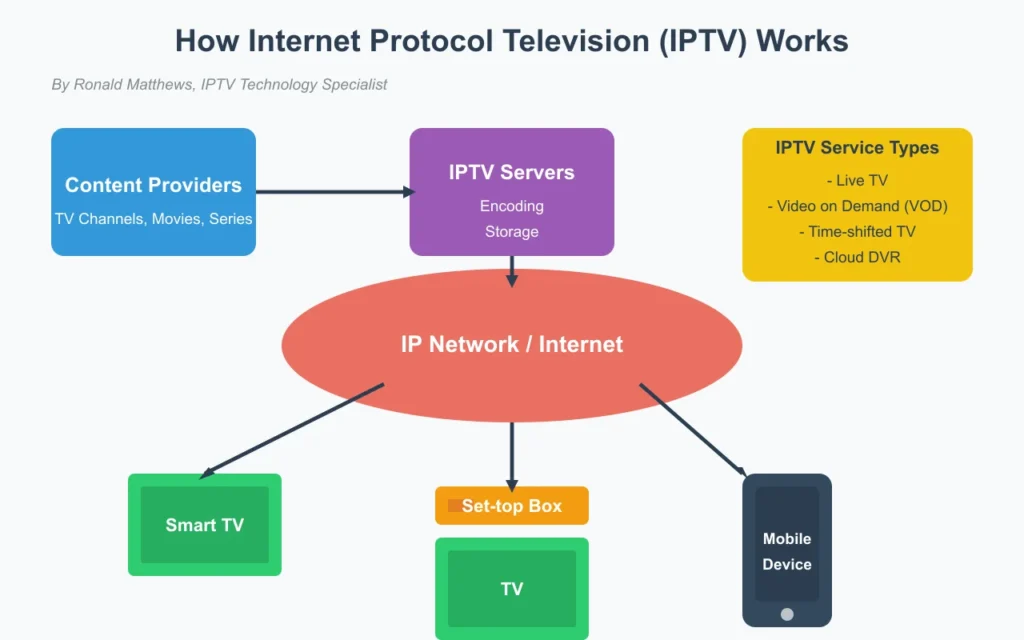
How Does IPTV Work? A Technical Breakdown
As an IPTV enthusiast and technology specialist, I find the technical aspects of IPTV fascinating. Let me break down how this system works:
Content Acquisition and Processing
The journey begins with content acquisition. IPTV providers acquire programming from various sources like TV networks, studios, and content creators. This content is then encoded and compressed into a digital format compatible with IP networks, preparing it for internet delivery.
The compressed video and audio signals are then sent through a dedicated group of servers that efficiently distribute the data to users while ensuring stable transfers. This encoding process is crucial as it significantly reduces the file size without drastically compromising quality, making it possible to stream high-definition content even on connections with limited bandwidth.
Network Architecture
IPTV requires a complex network setup to function effectively. At its core, it relies on a robust network infrastructure for seamless streaming. Many providers utilize fiber optic cables to form the backbone of their IPTV networks, ensuring high-speed data transmission.
The system employs IP multicasting, which allows simultaneous delivery to multiple viewers watching the same channel, reducing network load. For video-on-demand content, unicast connections are used, creating a direct stream from the server to the individual user.
Content Delivery to End Users
When a user selects content, the IPTV system initiates a stream. The video data travels from the provider's servers to the user's device. This process happens in real-time for live IPTV broadcasts. For on-demand content, the system retrieves stored video files from servers.
To enjoy IPTV, end-users need:
- A reliable internet connection – essential for streaming
- Access to software that will manage the IPTV channels to which they're subscribed
- A set-top box (which receives and decodes the IP packets into a signal a TV screen can display) or a compatible app on smart TVs, computers, or mobile devices
The Streaming Process Simplified
Here's how the process works from a user perspective:
- You select a channel or program through your IPTV interface
- Your device sends a request to the streaming server
- The server validates your request and begins sending the requested content in small data packets
- These packets travel through the internet to reach your device
- Your device (set-top box or app) reassembles these packets and decodes them
- The decoded content displays on your screen in real-time
This entire process happens in seconds, creating a seamless viewing experience when everything works correctly.
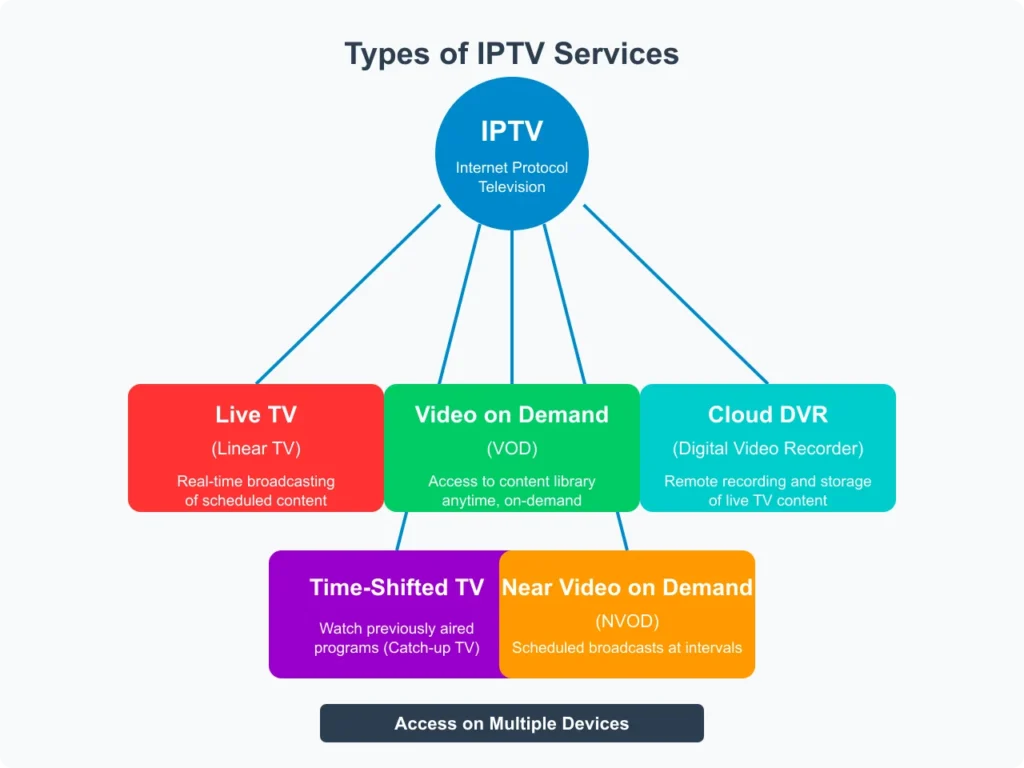
Types of IPTV Services: Understanding Your Options
As an IPTV specialist who's worked with various service models, I can tell you that IPTV offers several distinct types of services, each catering to different viewing preferences:
Live TV (Linear TV)
Live TV in an IPTV context refers to streaming television broadcasts in real-time over the internet, similar to traditional TV. This service allows viewers to watch programming as it's being aired, just like conventional broadcast television but delivered via internet protocol.
The key difference is that unlike traditional TV, live IPTV channels allow viewers to watch from anywhere, as long as they have internet access. Users may even pause or rewind live broadcasts, something impossible with conventional broadcasting.
Video on Demand (VOD)
This is perhaps the most recognizable and common type of IPTV service. VOD allows users to select and watch video content whenever they want from a vast library of options. Users can browse, search, and filter content, then watch it at their convenience.
VOD services give complete control over viewing schedules, allowing users to pause, rewind, fast-forward, and re-watch content as desired. This type of service has revolutionized how we consume media, breaking the constraints of scheduled programming.
Time-Shifted TV
Time-shifted IPTV, also known as catch-up TV, allows users to watch previously broadcasted shows at a later time. This feature differs from Video on Demand since catch-up TV typically only offers content for a limited period after the original broadcast.
Key features include:
- Pause and Resume: Pause live TV and resume watching from where you left off
- Rewind and Fast-Forward: Go back to re-watch a scene or skip ahead during a live broadcast
- Catch-Up TV: Watch programs that have aired in the past few days or weeks, even if you didn't record them
Services like BBC iPlayer, Hulu, and SuperBOX offer excellent time-shifted capabilities, allowing viewers to catch up on their favorite shows at their convenience.
Near Video on Demand (NVOD)
NVOD allows users to watch scheduled broadcasts of movies or shows at different time intervals. Unlike true VOD, NVOD offers multiple start times for the same program, similar to an online movie theater.
This can be a great source of revenue since ads can be included at interval breaks of the NVOD's programming schedule. This, in turn, allows providers to offer minimal subscription fees that benefit users.
DirecTV and Dish Network provide NVOD services, particularly to their rural customer base who might only have access to slower internet options.
Cloud DVR (Digital Video Recorder)
Cloud DVR functionality allows users to record live television and store it in the cloud, rather than on a physical hard drive. This service enables viewers to:
- Record multiple programs simultaneously
- Set recordings remotely using a mobile app or web interface
- Access recordings from any compatible device
- Store more content compared to traditional DVRs
Many IPTV subscription packages now include Cloud DVR features, enhancing the flexibility and convenience of the service.
The Technical Infrastructure Behind IPTV
As someone passionate about the technology that powers IPTV, I find the infrastructure particularly interesting. Let's look at the key components that make IPTV possible:
Content Servers and Storage Systems
At the heart of any IPTV system are powerful content servers that store and manage all programming. These servers house thousands of hours of content, from live feeds to on-demand movies and shows. They're designed to handle vast amounts of data and facilitate simultaneous streams to thousands or even millions of users.
The storage infrastructure must be robust, scalable, and redundant to ensure uninterrupted service. Many providers utilize distributed storage systems across multiple data centers to protect against outages and ensure content availability.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs play a crucial role in IPTV delivery, distributing content across multiple servers in various geographic locations. This reduces latency by serving content from the server closest to the end-user, resulting in faster loading times and smoother playback.
By spreading the load across numerous servers, CDNs also help prevent system overloads during peak viewing times, such as during major sporting events or popular show premieres.
Middleware and User Interfaces
IPTV middleware serves as the bridge between the content servers and the end-user applications. It manages user authentication, content rights, streaming protocols, and more. The middleware also powers the user interface – what viewers interact with when selecting channels or content.
A well-designed user interface is crucial for IPTV adoption. The best interfaces are intuitive, responsive, and provide features like personalized recommendations, search functionality, and parental controls.
Quality of Service (QoS) Management
Unlike OTT services that run over the public internet, many IPTV providers operate on managed networks that implement strict Quality of Service controls. These controls prioritize video traffic to ensure consistent streaming quality, minimizing buffering and interruptions.
QoS management becomes particularly important for live events where any delay or disruption can significantly impact the viewing experience. Advanced IPTV systems incorporate real-time monitoring and adaptive streaming technologies to maintain optimal quality regardless of network conditions.

Benefits of IPTV: Why Users Are Making the Switch
Having guided many clients through their transition to IPTV systems, I've seen firsthand the numerous advantages this technology offers:
Unprecedented Content Access and Flexibility
IPTV transforms the way viewers access entertainment by offering thousands of live TV channels, movies, and series from around the world. This vast selection covers diverse genres, including sports, news, entertainment, and international content, allowing viewers to explore global programming and expand their cultural horizons.
The platform accommodates different tastes within a household, making it possible for parents to find educational content for children, teenagers to access youth-oriented programming, and adults to enjoy more mature content. This eliminates the need for multiple subscriptions or services, providing a one-stop solution for all entertainment needs.
On-Demand Viewing and Time Control
The on-demand feature of IPTV completely transforms the viewing experience. Users can watch content at any time, free from traditional broadcast schedules. This flexibility accommodates busy lifestyles and varying routines – no more rushing home for favorite shows or missing important content due to scheduling conflicts.
IPTV puts users in control of their viewing experience with pause, rewind, and fast-forward functions. This control extends to the pace of consumption, allowing viewers to watch episodes back-to-back for binge sessions or space them out as desired.
The reduced reliance on traditional broadcast times benefits various groups, from shift workers who can enjoy prime-time shows outside standard hours to parents who can watch adult content after children's bedtimes.
Superior Streaming Quality
Modern IPTV services deliver exceptional streaming quality, with many providers offering HD and 4K streaming options. These high-resolution formats ensure crisp, clear visuals that are particularly impressive on large screens and modern TVs.
The streaming quality remains consistent thanks to advanced technologies that reduce buffering and lag during playback. Many IPTV platforms also adapt streaming quality based on internet speed, ensuring optimal performance across various connections.
Audio quality isn't overlooked either, with many services offering surround sound options that elevate the overall viewing experience, especially for movies and live events. The combination of high-quality video and audio creates a truly cinematic experience at home.
Multi-Device Compatibility
One of IPTV's most appreciated features is its multi-device compatibility. The service works seamlessly across smart TVs, computers, tablets, and smartphones, allowing users to access their favorite content on any device without quality compromise.
This versatility supports on-the-go content consumption – commuters can watch shows on smartphones during travel, while travelers can access familiar programming on laptops in hotel rooms, ensuring entertainment is always available regardless of location.
IPTV improves convenience through device-switching capabilities, allowing viewers to start a show on their TV and continue on a tablet without interruption. The platform also supports multiple users accessing different content on various devices simultaneously, eliminating conflicts over shared TV time.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Traditional Services
An IPTV subscription is typically more affordable than traditional cable or satellite services while offering extensive content. This pricing structure reduces overall entertainment costs for consumers, allowing households to access a wide range of programming without breaking the bank.
The service eliminates many hidden fees associated with traditional providers – no equipment rental charges, installation costs, or unexpected price hikes common with cable contracts. This transparency in pricing allows for better budget planning.
IPTV encourages subscription flexibility through various package options, allowing users to choose plans that align with their viewing habits and preferences. This customization ensures consumers only pay for the content they want, eliminating the need for expensive, all-inclusive packages with unused channels.

The Different IPTV Provider Models: Choosing the Right Service
As an IPTV specialist who's evaluated numerous providers and subscription options, I can offer insights into the different types of IPTV services available:
Traditional IPTV Providers
These are often established telecommunications companies or TV service providers that have expanded into IPTV. They typically offer IPTV as part of a bundled service that may include internet, phone, and other services.
Traditional providers usually operate over managed networks, ensuring quality of service, and offer set-top boxes for a traditional TV viewing experience. Examples include AT&T TV, Verizon Fios TV, and similar services from major telecom companies.
OTT-Based IPTV Services
These providers offer live channel packages along with on-demand content, accessible through apps on smart TVs, streaming devices, computers, and mobile devices.
In this article, I explain how to select the best IPTV provider based on content quality, reliability, device compatibility, customer support, and value for money.
Specialized IPTV Subscription Services
Some IPTV providers specialize in particular content types or markets:
- Sports-focused services
- International content providers that specialize in programming from specific countries or regions
- Niche content providers focusing on particular genres or interests
When selecting an IPTV provider, it's crucial to consider factors like content offerings, streaming quality, device compatibility, pricing structure, and most importantly, the legality of the service.

Legal Considerations and Choosing a Legitimate IPTV Subscription
As someone who prioritizes both quality and legality in the IPTV space, I must emphasize the importance of using legitimate IPTV services:
Understanding Legal vs. Illegal IPTV Services
The legality of IPTV hinges on the specific service and its licensing arrangements:
- Legal IPTV Services: These are provided by companies that have secured the necessary licenses to distribute content. They operate within copyright laws and typically involve a subscription fee that compensates content creators and distributors appropriately.
- Unauthorized IPTV Services: Some services offer copyrighted content without proper licensing, which is illegal. These often lure users with suspiciously low prices but carry significant risks, including unreliable service, potential malware, and legal consequences for the user.
How to Identify Legitimate IPTV Providers
When searching for an IPTV provider, look for these signs of legitimacy:
- Transparent Business Operations: Legitimate companies have clear contact information, terms of service, and privacy policies.
- Reasonable Pricing: If a deal seems too good to be true (like hundreds of premium channels for a few dollars a month), it probably is.
- Professional Website and Customer Support: Legitimate services invest in their online presence and customer support systems.
- Clear Content Licensing Information: Many legitimate providers proudly display their partnerships with content creators and distributors.
- Payment Processing: Legitimate services typically use standard, secure payment methods rather than obscure payment systems.
Using unauthorized IPTV services not only potentially exposes you to legal risks but also undermines the content creation industry, ultimately resulting in less content being produced.
The Future of IPTV Technology
As someone deeply passionate about IPTV technology, I'm excited about where this field is heading. Here are some developments we can expect to see:
Integration with Emerging Technologies
IPTV is increasingly integrating with other cutting-edge technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is enhancing content recommendations, creating more personalized viewing experiences, and even optimizing streaming quality based on viewing patterns and network conditions.
- Voice Control and Smart Home Integration: Voice commands are becoming a standard feature for IPTV systems, allowing viewers to search for content, change channels, and control playback without a remote. Integration with wider smart home ecosystems is also growing.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Some providers are experimenting with VR and AR features, offering immersive viewing experiences for certain types of content.
Enhanced Interactive Features
The interactive capabilities of IPTV continue to evolve:
- Advanced Social Features: Integrated chat, social media sharing, and collaborative watching experiences are becoming more common.
- Interactive Content: Programming that allows viewers to influence outcomes, choose different storylines, or access additional information about what they're watching.
- Second Screen Experiences: Synchronized content on mobile devices that complements what's playing on the main screen, enhancing sports, educational content, and more.
Improved Video Quality and Efficiency
Technical advancements continue to improve the viewing experience:
- 8K Resolution Support: As 8K displays become more common, IPTV providers will adapt to support this ultra-high resolution.
- Advanced Compression Technologies: New video codecs like AV1 promise better quality at lower bitrates, making high-quality streaming more accessible even with limited bandwidth.
- Reduced Latency: Innovations in streaming technology are reducing the delay between live events and their appearance on screen, crucial for sports and live events.
Setting Up Your Own IPTV System: A Basic Guide
Based on my experience helping clients set up their IPTV systems, here's a simplified guide for those interested in getting started:
Required Hardware and Software
To access IPTV services, you'll need:
- A Reliable Internet Connection: For HD content, I recommend at least 10 Mbps download speed, while 4K content may require 25 Mbps or more.
- A Compatible Device: This could be:
- A smart TV with built-in IPTV apps
- A dedicated IPTV set-top box
- A general-purpose streaming device (like Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV, or Roku)
- A computer, tablet, or smartphone
- IPTV Software or App: Depending on your chosen device, you'll need an appropriate app to access your IPTV subscription.
Selecting the Right IPTV Subscription
When choosing an IPTV provider, consider:
- Content Selection: Ensure the service offers the channels and content you're interested in.
- Streaming Quality: Check what resolutions are supported (HD, Full HD, 4K).
- Device Compatibility: Verify that the service works with your preferred viewing devices.
- Reliability: Research the provider's uptime and performance during peak hours.
- Customer Support: Good support is crucial if you encounter technical issues.
- Legal Standing: Ensure the provider operates legitimately with proper content licensing.
Optimizing Your IPTV Experience
To get the most from your IPTV setup:
- Use Wired Connections When Possible: Ethernet connections are generally more stable than Wi-Fi for streaming.
- Optimize Your Home Network: Consider quality routers, mesh Wi-Fi systems for larger homes, and keeping your streaming devices on the 5GHz band if using Wi-Fi.
- Close Bandwidth-Heavy Applications: When watching high-definition content, limit other bandwidth-intensive activities on your network.
- Consider a VPN: If your ISP throttles streaming traffic, a VPN might help (though it can sometimes cause other issues with certain IPTV services).
- Keep Your Devices Updated: Regular updates to your streaming device and IPTV app can improve performance and security.
Conclusion: The Continuing Evolution of Television Through IPTV
As we've explored throughout this article, Internet Protocol Television represents a significant evolution in how we consume visual media. As an IPTV enthusiast and technology specialist, I've witnessed firsthand how this technology has transformed from a niche service to a mainstream content delivery method that's challenging traditional television paradigms.
IPTV combines the best aspects of traditional television with the flexibility and user control of internet streaming. It offers unprecedented content choice, viewing flexibility, and device compatibility, all while potentially reducing costs compared to conventional cable or satellite services.
The technology continues to evolve rapidly, with improvements in streaming quality, user interfaces, and interactive features constantly enhancing the viewing experience. As internet infrastructure improves globally, IPTV's reach and capabilities will only expand.
Whether you're considering cutting the cord with traditional television services or simply looking to understand this technology better, I hope this guide has provided valuable insights into the world of IPTV. The future of television is increasingly internet-based, on-demand, and personalized – and IPTV stands at the forefront of this revolution.
About the Author: Ronald Matthews is a technology specialist with over 15 years of experience in digital content delivery systems, with particular expertise in IPTV technologies and implementation. He has consulted for numerous media companies and service providers on their transition to IP-based content delivery systems.





2 Responses